+86-18343147735
+86-18343147735 Which Blood Tests Are Essential for Your Annual Check-up?
An annual check-up is a proactive step for your long-term health. While many Americans get a yearly exam, understanding the blood lab tests involved is crucial. These tests provide a vital snapshot of your health. They can spot issues before they become serious, especially with chronic diseases on the rise.
Did You Know? 💡 An estimated 129 million people in the U.S. have at least one major chronic disease. These conditions include heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure.
Four foundational blood tests are essential for your check-up. They are the Complete Blood Count (CBC), Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP), Lipid Panel, and Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). These tests check your organ function, metabolic status, and risk for common diseases. Some doctors may also recommend an Infectious Diease Test Kit for HIV Test Kit, Dengue Test Kit, Tuberculosis Test Kit based on your individual risk factors. These initial blood lab tests give you and your doctor valuable information to manage your health effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Annual blood tests are important. They help you and your doctor understand your health. They can find problems early.
- Four main tests are key. These are CBC, CMP, Lipid Panel, and HbA1c. They check your organs, metabolism, and disease risks.
- Prepare for your tests. Follow fasting rules if needed. Talk to your doctor about medicines. This helps get accurate results.
The Foundational Four: Essential Annual Blood Tests
Your annual check-up relies on four key tests to paint a picture of your health. These foundational blood lab tests give your doctor a baseline. They help track changes in your body over time. Let's explore the first two: the Complete Blood Count and the Comprehensive Metabolic Panel.
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) is a standard test during your annual physical. It measures the main components of your blood. This test provides a broad overview of your health. It counts your red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
A CBC helps your doctor screen for a wide range of conditions.
- Anemia: Low red blood cell counts can indicate anemia. This means your body may not get enough oxygen.
- Infection: A high white blood cell count often signals that your body is fighting an infection.
- Immune System Disorders: Abnormal white blood cell levels can point to issues with your immune system.
- Blood Cancers: Unusual counts may be an early sign of certain blood cancers like leukemia.
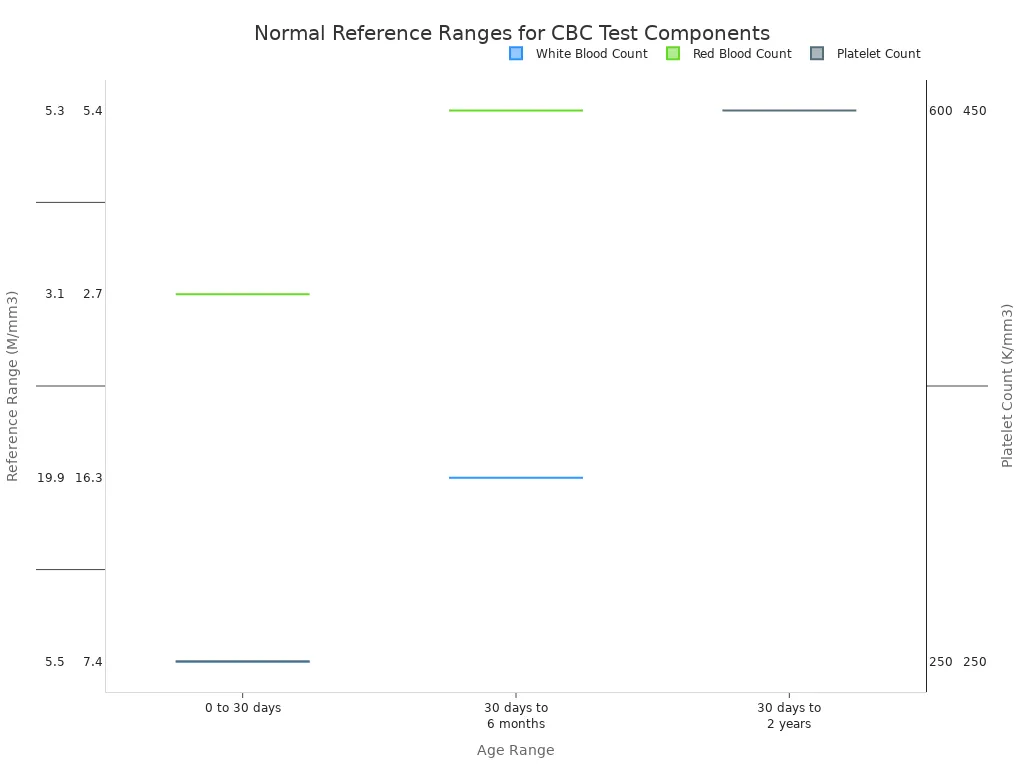
Your results are compared to a normal reference range. These ranges can vary based on age and sex. For adults, the typical ranges are:
| Component | Normal Adult Reference Range |
|---|---|
| White Blood Cells (WBC) | 3,500 to 11,000 cells/mm³ |
| Red Blood Cells (RBC) | 4.0 to 6.1 million cells/mm³ |
| Platelets | 150,000 to 450,000/mm³ |
Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)
The Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP) is another one of the essential blood lab tests. It measures 14 different substances in your blood. This panel gives your doctor important information about your body's chemical balance and metabolism. It is a key tool for checking your organ function.
The CMP looks at several key areas:
- Kidney and Liver Function: It measures proteins and waste products to see how well these organs are working.
- Blood Sugar: The glucose level helps screen for diabetes or prediabetes.
- Electrolyte and Fluid Balance: It checks levels of important minerals like sodium, potassium, and calcium.
The table below explains what some of these measurements mean for your liver and kidney health.
| Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| BUN & Creatinine | These are waste products. High levels may indicate your kidneys are not filtering blood properly. |
| ALT & AST | These are enzymes found mostly in the liver. High levels can signal liver damage. |
| Albumin | This is a protein made by your liver. Low levels can point to liver or kidney issues. |
What Do Abnormal Levels Mean? 💡 Your CMP results can reveal important health clues. High glucose may suggest a risk for diabetes. Abnormal calcium levels can point to bone, thyroid, or kidney conditions. Imbalances in electrolytes like sodium and potassium might indicate dehydration, kidney disease, or heart problems. Your doctor will interpret these results in the context of your overall health.
Key Blood Lab Tests for Risk Factors
Beyond checking your general organ function, some blood lab tests look for specific risk factors. Two of the most important are the Lipid Panel And the Hemoglobin A1c. These tests help you and your doctor understand your risk for heart disease and diabetes, two of the most common chronic conditions.
Lipid Panel (Cholesterol Test)
A Lipid Panel is a test that measures the amount of fats, or lipids, in your blood. You might know it as a cholesterol test. This panel is crucial for assessing your risk of developing heart disease and stroke. Between 2017 and 2020, about 10% of adults over age 20 had high total cholesterol, showing how common this issue is. The prevalence is highest for adults aged 40-59, at 16.7%.
The test measures several key components in your blood:
| Lipid Type | What It Is & What It Does |
|---|---|
| Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) | This is the "bad" cholesterol. High levels can build up in your arteries, increasing heart attack and stroke risk. |
| High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) | This is the "good" cholesterol. It helps remove bad cholesterol from your body, lowering your risk for heart disease. |
| Triglycerides | These are another type of fat in your blood. High levels can also raise your risk for heart disease. |
Good to Know: Fasting Isn't Always Needed 💡 In the past, you always had to fast before a lipid panel. Today, doctors know that non-fasting tests are just as accurate for most people. Your doctor will tell you if you need to fast. It's also helpful to know that your cholesterol levels are often stable for years. Other factors like your weight, blood pressure, and smoking habits have a bigger impact on your overall heart disease risk score.
Your doctor uses your lipid panel results to decide on the best plan for you. Different organizations, like the American College of Cardiology (ACC), have guidelines to help. Your doctor will combine your test results with your personal risk factors to make recommendations.
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)
The Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test is the primary tool for diagnosing and monitoring diabetes. Unlike a standard glucose test that measures your blood sugar at a single moment, the HbA1c test provides a bigger picture. It shows your average blood sugar level over the past two to three months. This makes it a much more reliable indicator of your long-term glucose control.
The results of your HbA1c test fall into one of three categories. These results tell you and your doctor if your blood sugar is in a healthy range.
| Diagnosis | A1C Level |
|---|---|
| Normal | Below 5.7% |
| Prediabetes | 5.7% to 6.4% |
| Diabetes | 6.5% or above |
Receiving a prediabetes diagnosis means your blood sugar is higher than normal. You can see this as an important warning sign. It gives you an opportunity to make lifestyle changes, like improving your diet and exercising more, to prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes. A result of 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes, which requires a plan developed with your doctor to manage your health.
Additional Tests to Discuss With Your Doctor
The foundational four tests provide a great overview, but they don't tell the whole story. Your doctor may recommend other blood lab tests based on your age, family history, or specific symptoms. Chronic fatigue, a family history of thyroid disease, or a high Body Mass Index (BMI) might lead your doctor to look deeper.
Thyroid Panel (TSH)
Your thyroid gland controls your metabolism. A Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) test checks if it is working correctly. Thyroid disorders are quite common, affecting about 5% of the U.S. adult population. They become more frequent as you get older.
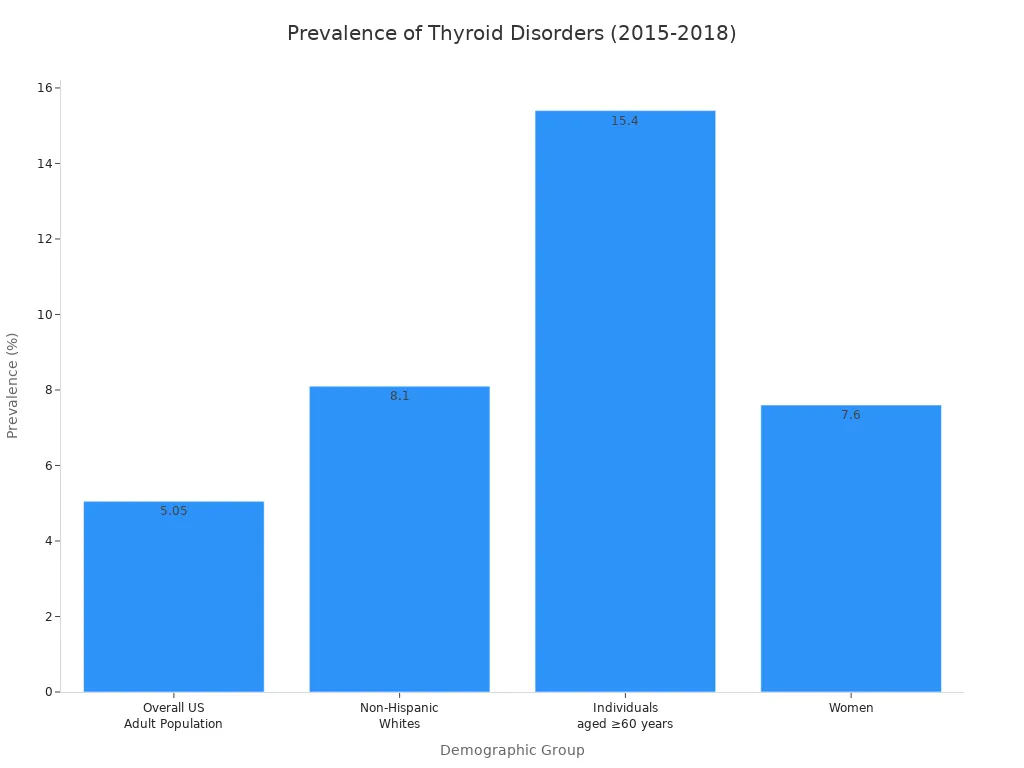
Your doctor may order this test if you experience symptoms like unexplained weight changes or fatigue.
| Condition | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Hyperthyroidism (Overactive) | Weight loss, rapid heartbeat, nervousness |
| Hypothyroidism (Underactive) | Weight gain, fatigue, sensitivity to cold |
Vitamin and Mineral Levels
Many people have low levels of important vitamins and minerals without knowing it. Deficiencies in Vitamin D and B12 are especially common. These can cause symptoms like body aches, brain fog, and constant tiredness. A simple blood test can check your levels and help you find a solution.
High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein (hs-CRP)
The high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) test measures low-level inflammation in your body. Chronic inflammation can contribute to the buildup of plaque in your arteries. This test helps assess your risk for heart disease.
Know Your Risk Level 💡 The American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association consider an hs-CRP level of 2.0 mg/L or higher a "risk enhancer." This result can help you and your doctor make decisions about managing your heart health, such as starting or adjusting statin therapy.
Discussing these additional blood lab tests with your provider helps create a more complete picture of your health.
How to Prepare for Your Blood Draw
Proper preparation helps ensure your blood test results are accurate. A few simple steps can make the process smoother and provide your doctor with the best information. Getting a good night's sleep and drinking plenty of water before your test can make it easier for the phlebotomist to find a vein.
Understanding Fasting Requirements
Some blood lab tests require you to fast. This means you should not eat or drink anything except water for 8 to 12 hours before your blood draw. Fasting is often necessary for tests like the Lipid Panel and Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP). It ensures that recently eaten food does not affect your glucose or triglyceride levels.
A Quick Tip 💡 Avoid coffee, tea, and other caffeinated drinks before your test, even if you are fasting. Caffeine can dehydrate you, which might affect your results. Stick to plain water.
Medications and Supplements
You should tell your doctor about all medications and supplements you take. Some common supplements can interfere with test results.
- Biotin (Vitamin B7): High doses can affect thyroid test results.
- Creatine: This can raise creatinine levels, a marker for kidney health.
- Certain Antibiotics: Some can impact glucose or kidney function results.
Your doctor will give you specific instructions. You may need to stop taking a supplement for a few days before your test. Always continue taking prescribed medications unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
What to Discuss Before Your Test
Asking questions helps you feel prepared and confident. It ensures you and your doctor are on the same page. Here are a few key things to ask before your blood draw:
- What is this test measuring?
- Do I need to fast for this test?
- Should I take my daily medications and supplements as usual?
- When and how will I get my results?
This conversation helps you play an active role in your healthcare.
Your annual check-up starts with four key blood lab tests. The CBC, CMP, Lipid Panel, and HbA1c form your health baseline. Talk with your doctor about these results and other tests you may need. This teamwork helps you build a strong plan for your long-term wellness and take control of your health.
FAQ
How often should I get these blood tests?
You should get these foundational tests each year. Your doctor uses the results to monitor your health over time and spot changes early.
What happens if my test results are abnormal?
Your doctor will discuss any abnormal results with you. You may need follow-up tests or a new plan to manage your health effectively.
Does insurance cover these annual blood tests?
Most insurance plans cover preventive care like annual blood work. You should always check with your insurance provider to understand your specific coverage details.